Understanding Hip Osteoarthritis: Causes and Symptoms
Hip osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly as they age. It is a degenerative joint disease that primarily impacts the cartilage surrounding the hip joint, causing pain, stiffness, and discomfort. While this condition can significantly affect daily activities, understanding its causes and symptoms can help manage it effectively and seek appropriate medical care.
What is Hip Osteoarthritis?
It occurs when the cartilage in the hip joint wears down over time. This cartilage acts as a cushion between the bones of the hip, allowing for smooth and pain-free movement. When it wears away, the bones in the joint begin to rub against each other, causing pain, inflammation, and restricted movement.
This condition is more common among older adults, but it can also develop in younger individuals due to specific risk factors such as injury or genetic predisposition. Managing hip osteoarthritis is essential to improving mobility and reducing pain, and early diagnosis plays a critical role in effective treatment.
Causes of Hip Osteoarthritis
Several factors contribute to the development of hip osteoarthritis, including:
Age: As people age, the natural wear and tear on the joints increase, making osteoarthritis more common in individuals over 50.
Genetics: If your family has a history of osteoarthritis, you may be more prone to developing the condition yourself.
Previous Injuries: Any previous injuries to the hip, such as fractures or dislocations, can accelerate the wear and tear of the joint, leading to osteoarthritis.
Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional pressure on the hip joints, speeding up the degeneration of cartilage.
Repetitive Stress: Jobs or activities that require repetitive movements of the hip joint, such as manual labor or sports, can increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis.
Congenital Hip Dysplasia: Some people are born with abnormalities in the hip joint, which can cause the cartilage to wear away more quickly.
Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation in the joints, which can lead to osteoarthritis.
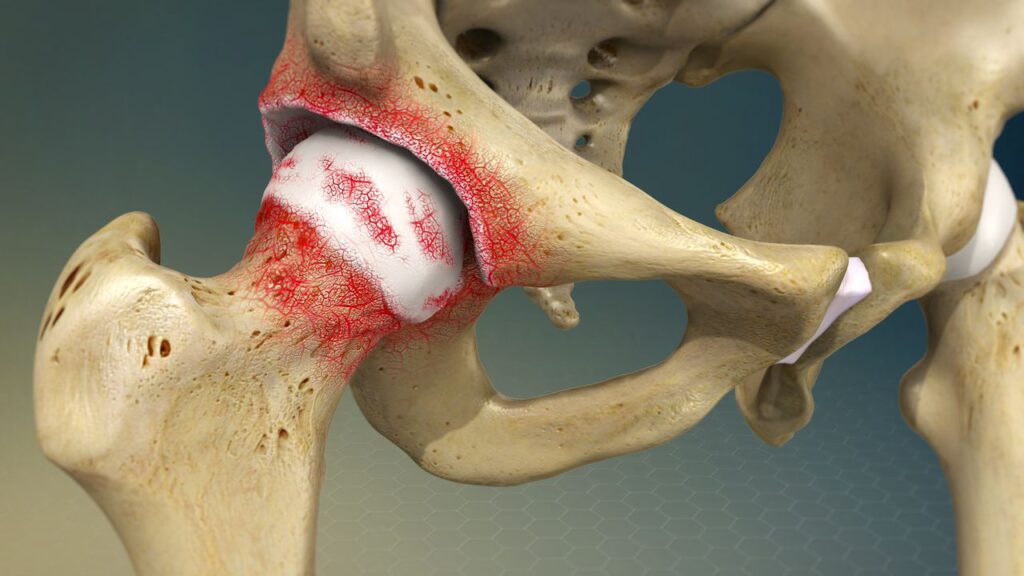
Symptoms of Hip Osteoarthritis
Recognizing the symptoms of hip osteoarthritis early can help manage the condition better. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
Pain in the Hip: One of the first and most noticeable symptoms is pain in the hip joint. This pain may start as a mild ache but can become more severe over time. The pain is often felt in the groin, thigh, or buttocks, and it may worsen after periods of inactivity or strenuous physical activity.
Stiffness: Many people with hip osteoarthritis experience stiffness in the joint, particularly in the morning or after sitting for a long period. This stiffness can make it difficult to move the hip freely.
Reduced Range of Motion: As the condition progresses, you may notice a decrease in the range of motion in your hip. Activities such as bending, walking, or climbing stairs can become more challenging.
Swelling and Tenderness: The hip joint may become swollen and tender to the touch due to inflammation caused by the degeneration of cartilage.
Grinding Sensation: Some individuals report a grinding or clicking sensation in the hip joint when they move, which can indicate cartilage damage.
Limping: Over time, the pain and stiffness caused by hip osteoarthritis can lead to limping, as you may unconsciously shift your weight to the opposite side to reduce discomfort in the affected hip.
When to Seek Help
If you experience any of the above symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical advice from an orthopedic specialist. Early diagnosis and treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and improve your quality of life.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for hip osteoarthritis, several treatment options can help manage the symptoms. These include:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint can help improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can provide relief from symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding activities that place excessive strain on the hip can help manage osteoarthritis.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, hip replacement surgery may be recommended to relieve pain and restore function.
Conclusion
It can be a painful and limiting condition, but with the right approach, its impact can be minimized. Recognizing the causes and symptoms early and seeking timely treatment is vital to managing the condition effectively.
For expert diagnosis and treatment of Hip Osteoarthritis, visit Dr. Tushar Anand, Best Orthopedic Surgeon in Meerut. He offers personalized care and advanced solutions to help patients regain their mobility and quality of life.
faqs:
The early signs of hip osteoarthritis include pain in the hip joint, stiffness after periods of inactivity, reduced range of motion, and occasional swelling or tenderness in the hip. Pain is often felt in the groin, thigh, or buttocks and may worsen with physical activity.
Yes, it can be managed without surgery in many cases. Treatment options include physical therapy, medications, lifestyle changes (such as weight management), and low-impact exercises. Surgery, such as hip replacement, is generally considered only when these methods are ineffective.
The main causes of hip osteoarthritis include age-related wear and tear, previous hip injuries, genetic predisposition, obesity, repetitive stress on the hip joint, and conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or congenital hip dysplasia.

