Meniscus Tear: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
By Dr. Tushar Anand, Orthopedic Surgeon
A meniscus tear is a common knee injury that can cause pain and affect mobility. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for proper management and recovery. This article will explore the key aspects of a meniscus tear and provide guidance on what to do if you experience this injury.
What is a Meniscus Tear?
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage in the knee joint that acts as a cushion between the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci – one on the inner side (medial meniscus) and one on the outer side (lateral meniscus). These structures help to stabilize the knee and absorb shock during activities like walking, running, and jumping.
A meniscus tear occurs when this cartilage is damaged due to forceful twisting or rotation of the knee. This type of injury is common among athletes, especially those involved in sports that require sudden changes in direction, such as football, basketball, and tennis. However, meniscus tears can also occur in older adults due to degeneration of the cartilage.
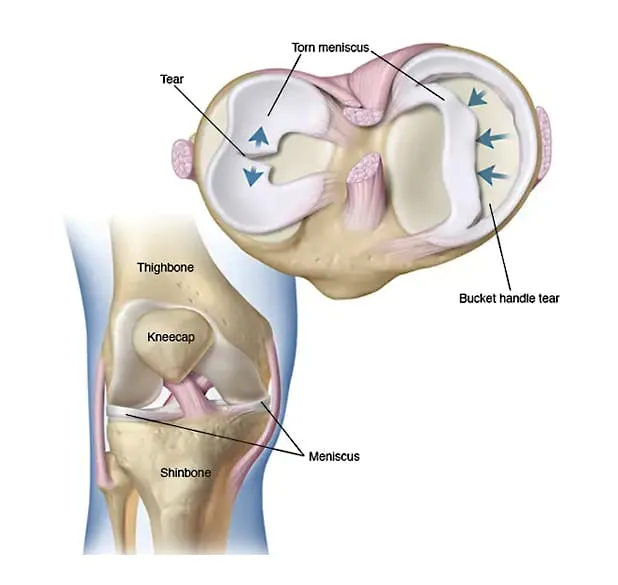
Causes of Meniscus Tear
- Trauma: A sudden twist or turn of the knee, often during sports activities, can cause a meniscus tear. This is particularly common when the foot is planted, and the knee is twisted.
- Degeneration: As we age, the meniscus weakens and becomes more prone to tears, even from minor movements. Degenerative meniscus tears are common in older adults.
- Direct Impact: A direct blow to the knee, such as during a car accident or a fall, can also lead to a meniscus tear.
Symptoms of Meniscus Tear
- Pain: The pain can vary in intensity and is often felt along the joint line. It may worsen with twisting or rotating the knee.
- Swelling: Swelling typically occurs within the first 24 hours after the injury.
- Stiffness: The knee may feel stiff and difficult to move.
- Locking Sensation: You might experience a sensation that your knee is locked in place and cannot be moved.
- Difficulty in Movement: Bending and straightening the knee can become challenging and painful.
Diagnosis
To diagnose a meniscus tear, an orthopedic doctor will conduct a physical examination and review your medical history. Specific tests, such as the McMurray test or the Apley grind test, may be performed to assess the injury. Imaging studies like X-rays or MRI scans are often used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of the tear.
Treatment Options
The treatment for a meniscus tear depends on the severity and location of the tear, as well as the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. Here are some common treatment options:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE): For minor tears, initial treatment involves resting the knee, applying ice to reduce swelling, using a compression bandage, and elevating the leg to decrease inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises can help improve knee stability and function. A physical therapist can design a personalized program to aid recovery.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Knee Bracing: Wearing a knee brace can provide support and prevent further injury.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can help reduce inflammation and pain in some cases.
- Surgery: If conservative treatments are ineffective or if the tear is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure where small instruments and a camera are inserted into the knee joint to repair or remove the damaged meniscus.
Recovery and Prevention
Recovery from a meniscus tear varies depending on the treatment approach and the individual’s healing process. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in regaining strength and mobility. It is important to follow the prescribed rehabilitation program to ensure a successful recovery.
To prevent meniscus tears, consider the following tips:
- Maintain Strong Muscles: Strengthening the muscles around the knee can provide better support and stability.
- Use Proper Techniques: Ensure proper techniques when participating in sports or physical activities.
- Warm Up: Always warm up before exercising to prepare your muscles and joints for activity.
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Choose shoes that offer good support and cushioning.
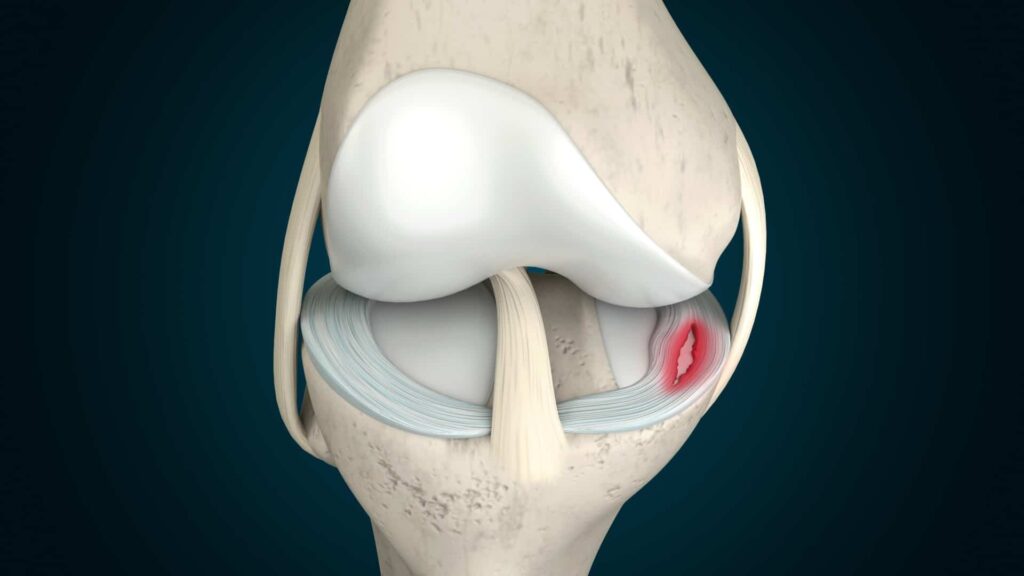
Conclusion
A meniscus tear can be a painful and debilitating injury, but with the right treatment and care, recovery is possible. If you suspect a meniscus tear, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent further damage and begin the healing process. For expert diagnosis and treatment, consider consulting an Orthopedic Doctor in Meerut.
faqs:
Symptoms of a meniscus tear include pain along the knee joint, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving the knee. You might also experience a locking sensation in the knee. If you suspect a meniscus tear, it’s important to consult with an orthopedic specialist who can perform a physical examination and possibly recommend imaging tests like an MRI to confirm the diagnosis.
Minor meniscus tears, especially those on the outer edge of the meniscus, can sometimes heal on their own with proper rest and conservative treatment like physical therapy. However, more severe tears, particularly those on the inner part of the meniscus, often require surgical intervention to heal properly. Consulting an orthopedic doctor is crucial to determine the best treatment plan based on the specific nature of the tear.
Recovery time from meniscus tear surgery can vary depending on the extent of the injury and the type of surgery performed. Generally, patients can expect to return to normal activities within 4 to 6 weeks after arthroscopic surgery. Physical therapy plays a significant role in the recovery process, helping to restore strength and mobility to the knee. Your orthopedic surgeon will provide a detailed rehabilitation plan tailored to your specific needs to ensure a successful recovery.